Did you know that a well-crafted technical report can make your research clear, credible, and impactful? Whether you’re documenting engineering experiments, presenting scientific data, or outlining project findings, a strong report transforms complex information into something structured and easy to understand.
But what exactly is a technical report, and why is it so important?
A technical report is a detailed document that conveys scientific or technical research objectively and practically. It is commonly used in engineering, agriculture, physical sciences, and biomedical research. Given the complexity of the information, a well-organized report ensures that findings are accessible and actionable.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key steps and structure of writing a technical report so you can present your work clearly and confidently!
How to Write a Technical Report
Writing a technical report can feel daunting, but it becomes much more manageable when you break it down into clear steps. So, how can you write a technical report that leaves the readers in a ‘wow’ mode? Let’s find out!

Understand the Purpose and Audience
The first step is to understand the purpose and audience. What is the goal of your report? Are you aiming to inform, persuade, or explain a technical concept? Identifying your objective will steer the direction and content of your report.
Gather and Organize Information
Once you understand your mission and audience, it’s time to gather your resources. This includes research findings, experimental data, technical specifications, or case studies relevant to your topic. Ensure you have all the necessary evidence and references to support your conclusions.
Read More: What is a Technical Proposal & How To Write One?
As you gather this information, organize it methodically. Create an outline using clear headings to structure your report. A common structure includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and optional recommendations.
Write the Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the rest of the document, providing context, background information, and an overview of the report’s objectives.
Always begin with a hook because your introduction should grab the reader’s attention. This could be a startling statistic, an intriguing question, or a relevant quote. The goal is to engage your audience right from the start. Then, you would want to Provide Background Information that sets the context for your report. This section should give the reader a brief overview of the topic and explain why it is essential.
Next would be the Statement of Purpose and Objectives, which helps the reader understand what to expect and sets the direction for the rest of the document. Be concise but specific about what your report aims to achieve.
It’s also important to define the scope of your report so that the reader knows what is included and what is not. This section should outline the boundaries of your study, including any limitations or exclusions.
Describe the Methodology
Here, you detail the methods and procedures used to gather data and conduct analysis. The description should be specific enough that someone could replicate your work.

Firstly you should outline your research design. This is the overall strategy you used to integrate the different components of your study in a coherent and logical way. Then you can detail the procedures you followed in conducting your research or project followed by explaining your data collection methods.
After data collection, what did you do next? Explain how you processed and analyzed the data and at the very end address limitations. No study is perfect. Discuss any limitations in your methodology that could affect your results.
Present the Results
Presenting results is a critical step in writing a technical report. This section showcases the outcomes of your work and forms the core of your report. It’s where your data, analysis, and insights come together to tell a coherent story.
You should always align your results with the objectives or hypotheses stated in your introduction. This ensures clarity and continuity. Break down your results into logical subsections using descriptive subheadings. This helps the reader navigate through your findings easily.
Utilize tables, graphs, and charts to present data visually. These tools can make complex data more understandable and highlight key trends and patterns. Also point out the most important and relevant result findings. Use bullet points or numbered lists to highlight key findings for easy reference.
Discuss the Findings
The discussion section goes beyond just presenting the results. Here, you delve deeper by interpreting and explaining their meaning and implications. Relate your findings to existing research or established theories and discuss any discrepancies or unexpected outcomes.
Explain how your results contribute to the field or address the problem stated in the introduction. Don’t forget to acknowledge any limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research or improvements. This strengthens your report and demonstrates a well-rounded understanding of the topic.

Conclude and Recommend
Finally, conclude with clarity and recommendations. Summarize the main points of your report and restate their importance. Avoid introducing new information here. If applicable, provide clear and concise recommendations based on your findings.
Offer practical solutions or propose the next steps. The conclusion should leave a lasting impression, solidifying the reader’s understanding of the report’s significance and its takeaways.
Format for Writing a Technical Report
A technical report follows a structured format to present information clearly, logically, and professionally. Below is a standard format with a narrative flow to make it more engaging and easier to follow.
1. Title Page
The title page serves as the first impression of your report. It should include the report’s title, the names of the author(s), and their affiliation, such as the company or institution they represent. Additionally, the date of submission should be clearly stated. If the report contains sensitive or proprietary information, a confidentiality statement should be included to protect its content.
2. Abstract
The abstract provides a concise summary of the entire report, typically between 150 to 250 words. It should highlight the objectives, methodology, key findings, and conclusions, offering readers a quick understanding of what the report entails. This section is particularly useful for those who need to grasp the essence of the report without diving into the full document.
3. Table of Contents
A well-organized table of contents helps readers navigate the report efficiently. It lists all major sections and sub-sections along with their corresponding page numbers, making it easy to locate specific information.
4. List of Figures and Tables (if applicable)
If the report includes multiple figures and tables, it is helpful to provide a dedicated section listing them along with their page references. This allows readers to find visual data quickly without having to skim through the entire document.

5. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the report by providing background information on the topic. It should clearly state the purpose and scope of the report, explaining why the subject matter is important. Additionally, it should introduce the problem or research question being addressed and offer a brief outline of how the report is structured.
6. Methodology
This section describes how the research or analysis was conducted. It should explain the data collection methods, whether through experiments, surveys, simulations, or other techniques. A justification for the chosen methodology is also essential, as it helps establish the credibility of the findings. Readers should gain a clear understanding of the approach taken to ensure transparency and reproducibility.
7. Results
Here, the findings of the study are presented in a clear and structured manner. Data should be displayed using well-labeled tables, graphs, or charts where necessary. The results should be explained objectively, without interpreting or drawing conclusions—this part is purely about presenting the facts.
8. Discussion
The discussion section delves into the meaning and significance of the results. It should interpret key findings, compare them with previous research or industry benchmarks, and highlight any patterns or unexpected outcomes. Any limitations of the study should also be acknowledged to provide a balanced perspective.
9. Conclusion and Recommendations
This section summarizes the main findings of the report and discusses their practical applications. It should reinforce the key takeaways and, if applicable, suggest recommendations for future research or improvements based on the findings. These recommendations can provide valuable insights for decision-makers or researchers looking to build on the work.
10. References
A well-documented reference section lists all the sources cited in the report. It should follow a specific citation style, such as APA, IEEE, or Harvard, ensuring that all references are properly formatted and credible.
11. Appendices (if needed)
Any additional material that supports the report but is too detailed for the main sections can be included in the appendices. This might include raw data, extensive calculations, technical specifications, or supplementary documentation that provides further context.
By following this structured approach, a technical report maintains clarity, professionalism, and logical flow, making it easier for readers to comprehend and act upon the presented information.
Read more: Technical Manual: What, Types & How to Create One? (Steps Included)
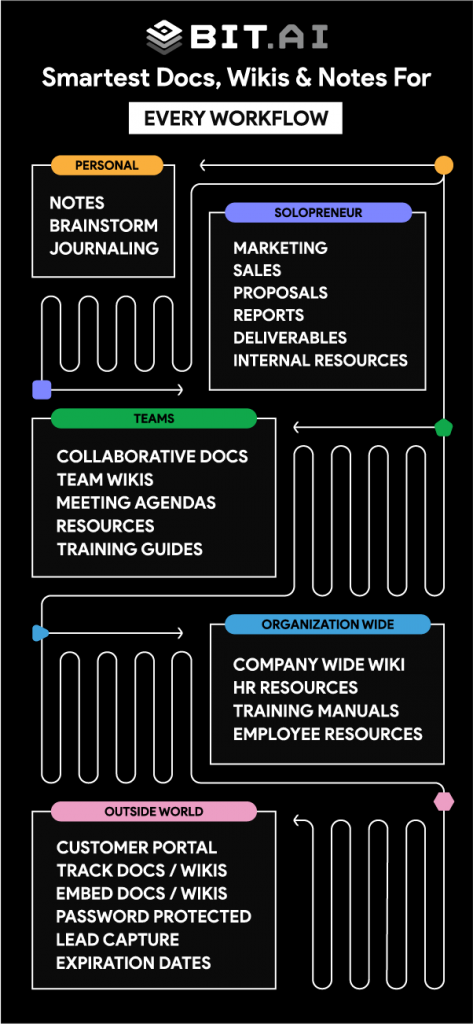
Why Choose Bit.ai for Writing Technical Reports
Let’s be honest—writing a technical report can feel like a daunting task. Whether you’re documenting an API, compiling product specifications, or drafting a research paper, the process often involves endless structuring, formatting headaches, and juggling feedback from multiple stakeholders.
What if there was a way to make technical writing smarter, faster, and more collaborative?
Meet Bit.ai, the all-in-one document collaboration platform designed to take the stress out of technical report writing. Bit transforms your reports from dry and tedious to structured, interactive, and engaging. Bit.ai offers a suite of features tailored to enhance the technical writing process:
AI- Writer & AI Powered Content Generation: Bit’s AI Genius Writer, with its 300+ prompts, assists in drafting well-structured content, ensuring your technical reports are coherent and professionally articulated.
Real-Time Collaboration: Facilitate teamwork with real-time co-editing, allowing multiple contributors to work simultaneously. Inline comments and @mentions streamline communication, ensuring all feedback is efficiently addressed.
Rich Media Integration: Enhance your reports by embedding various media types directly into your documents, providing a comprehensive and interactive experience for the reader.
Code Syntax Highlighting: For reports involving code, Bit.ai offers code blocks with syntax highlighting, ensuring that code snippets are presented clearly and professionally.
Automated Formatting and Templates: Utilize Bit’s extensive library of 100+ templates designed specifically for technical documents, such as API documentation, product requirements, and software design documents. These templates provide a structured format, allowing you to focus on content creation.
Document Tracking and Analytics: Monitor engagement with your reports through document tracking features, gaining insights into who has viewed your document and for how long, enabling you to assess the reach and impact of your work.
- Multiple Sharing Options: Share your reports as a living document, trackable document / wiki, password protection, link expiration, with lead capture, embed it on any website or intranet, and much more. You can also invite Guests into the platform to join your workspace, where they have to log in to view the content you wish to share with them.
See Bit.ai in Action
Curious about how it all comes together? Check out this Technical Report Example created with Bit.ai and see for yourself! So, the next time you need to write a technical report, why start from scratch? Let Bit.ai help this with you—so you can focus on delivering precise, professional, and polished reports with ease!
Examples of Technical Reports
Technical Research Report
Imagine a team of engineers working on a breakthrough in renewable energy. They conduct extensive testing on a new type of solar panel that promises 30% higher efficiency. To present their findings, they compile a technical research report, meticulously following a technical report format. The document includes an introduction explaining the purpose of the study, a methodology section detailing the experiments conducted, and a results section with data-backed conclusions. The technical report layout ensures clarity, allowing scientists, investors, and policymakers to quickly grasp the significance of the research.
Feasibility Report
A construction company is considering building an eco-friendly skyscraper in a densely populated city. Before moving forward, they commission a feasibility report, a crucial type of technical report writing. This report evaluates site conditions, construction costs, sustainability measures, and potential challenges. Using a standard technical report layout, it presents financial projections, environmental impact assessments, and engineering recommendations. Decision-makers rely on this structured analysis to determine whether the project is viable.
Business Proposal Report

A software startup wants to introduce an AI-driven cybersecurity solution for enterprises. To pitch their idea, they create a business proposal report, a structured document outlining their product’s functionality, market demand, and projected ROI. The technical report format ensures the report is clear, with sections dedicated to the problem statement, solution design, technical specifications, and potential risks. Investors reviewing the report can quickly assess its feasibility and make informed decisions.
User Guide/Manual
A tech company launches a new medical device that assists in remote patient monitoring. To ensure healthcare professionals can use it effectively, they develop a comprehensive user manual/guide, a form of technical report writing. This document includes step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting guides, and safety protocols. The technical report layout is designed for easy navigation, with headings, diagrams, and bullet points that enhance usability.
Progress Report
A government agency funds a nationwide smart traffic system to reduce congestion and accidents. Six months into the project, the development team submits a progress report detailing milestones achieved, current challenges, and upcoming phases. This type of technical research report provides stakeholders with an update, ensuring transparency and accountability. The structured technical report format ensures that all critical information is presented concisely, making it easier for executives to assess progress and make strategic adjustments.
Wrapping Up
Mastering the art of technical report writing is more than just following a structured format—it’s about transforming complex information into clear, accessible, and impactful communication. Whether you’re compiling research findings, drafting a feasibility study, or creating a user manual, a well-crafted report ensures that your message is understood and valued. By following the right steps, organizing your content effectively, and leveraging modern tools like Bit.ai, you can elevate your technical writing to a professional level. So, the next time you’re faced with a daunting report, remember: clarity, precision, and structure are your best allies. With the right approach, your technical report won’t just inform—it will inspire action, innovation, and meaningful decision-making!
FAQs
1. What is technical report writing?
Picture this: You’ve spent months researching the effects of solar energy on urban infrastructure. Now, how do you present your findings in a way that makes sense to engineers, policymakers, or corporate executives? That’s where technical report writing comes in. It’s a structured way of documenting complex information—complete with data, visuals, and analysis—to inform and guide decisions.
2. What is the format in a technical report?
Think of a technical report format as the blueprint of your document. It typically includes a title page, an abstract (like a sneak peek of what’s inside), an introduction (the ‘why’ behind the report), a methodology section (how you did the research), followed by results, discussions, conclusions, and references. The goal? To make sure your work is clear, structured, and easy to follow.
3. What are the five types of technical report writing?
Technical reports aren’t one-size-fits-all. There are five common types, each with a distinct purpose:
1. Technical Research Report: Presents findings from a detailed study or experiment.
2. Feasibility Report: Evaluates the practicality of a project or idea.
3. Business Proposal Report: Makes a case for a new initiative or investment.
4. User Guide/Manual: Provides step-by-step instructions on using a product or system.
5. Progress Report: Updates stakeholders on an ongoing project.
Further reads:
How To Create An Effective Status Report?
7 Types of Reports Your Business Certainly Needs!
What is Project Status Report Documentation?
Scientific Paper: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps and Format)
Business Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Format)
How to Write Project Reports that ‘Wow’ Your Clients? (Template Included)

Related posts
Bit.ai | Watch to Learn More
What is Bit.ai?
Bit.ai is an innovative AI-driven knowledge and Document Managment suite designed to empower knowledge workers by streamlining the creation of, documents, wikis, and notes. With an intuitive interface and seamless integration, Bit.ai acts as a versatile assistant to help you collaborate, generate, organize, and visualize your ideas effortlessly. Whether you are drafting a report, managing a project, collaborating with your team or clients, or brainstorming new concepts, Bit.ai brings intelligence and creativity to every aspect of your work process.